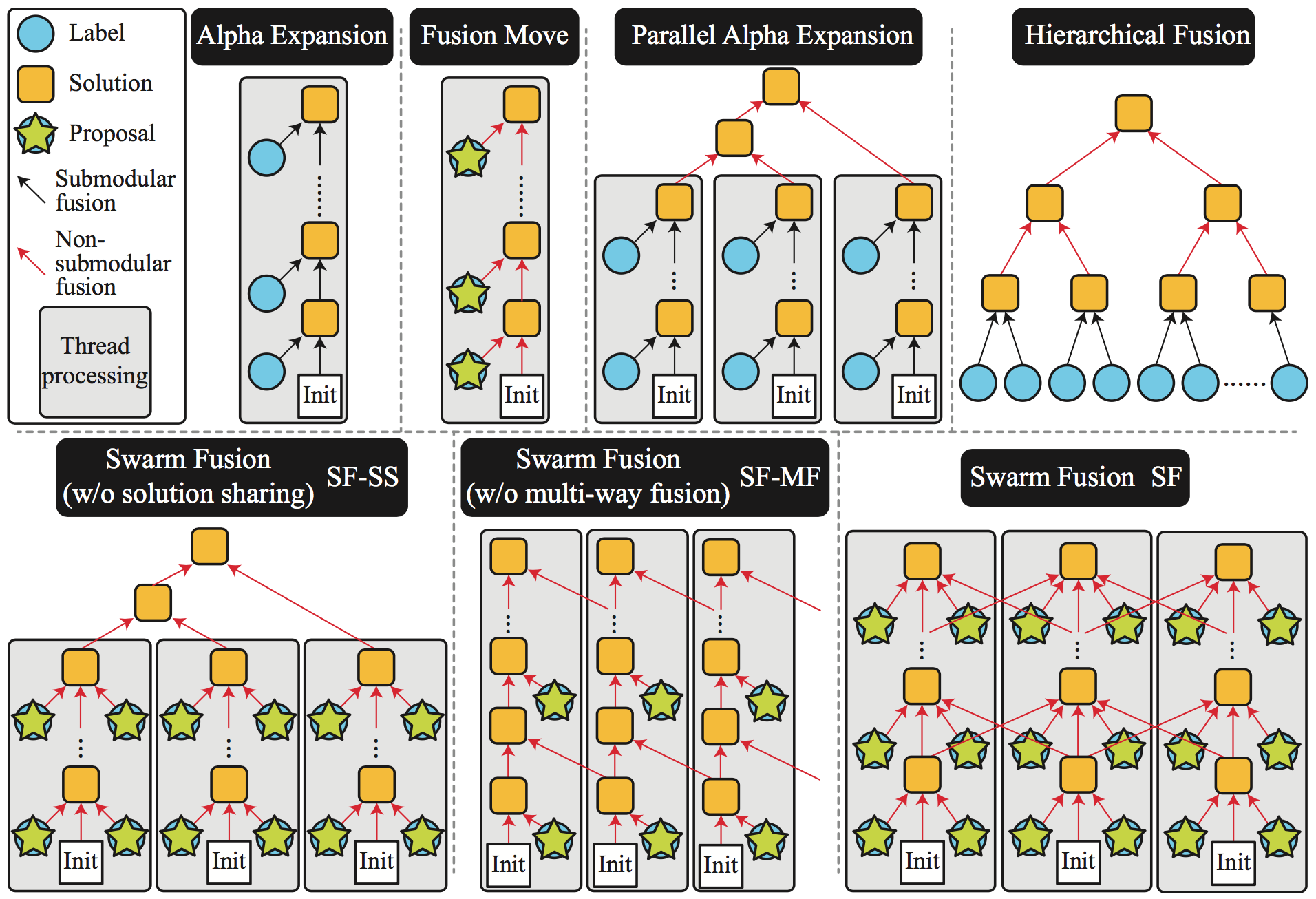
Figure 1: Swarm Fusion (SF) architecture and its relationships to existing methods. The bottom right example shows the general SF architecture, where each thread takes arbitrary number of solution proposals and concurrent solutions for fusion. The framework is flexible and can realize other data processing architectures depending on the parameters (e.g., the left two examples in the bottom row). It is easy to verify that existing popular MRF inference methods such as Alpha Expansion, Fusion Move, Parallel Alpha Expansion, and Hierarchical Fusion, are all special cases of SF.
Abstract
This paper proposes a novel MAP inference framework for Markov Random Field (MRF) in parallel computing environments. The inference framework, dubbed Swarm Fusion, is a natural generalization of the Fusion Move method. Every thread (in a case of multi-threading environments) maintains and updates a solution. At each iteration, a thread can generate arbitrary number of solution proposals and take arbitrary number of concurrent solutions from the other threads to perform multi-way fusion in updating its solution. The framework is general, making popular existing inference techniques such as alpha-expansion, fusion move, parallel alpha-expansion, and hierarchical fusion, its special cases. We have evaluated the effectiveness of our approach against competing methods on three problems of varying difficulties, in particular, the stereo, the optical flow, and the layered depthmap estimation problems.